Project management methodologies: key agile and traditional approaches to know
Estimated reading time : 20 minThe traditional approach: a linear project management method
The first approach to emerge in project management is the so-called traditional approach. It relies on a sequential, linear view of projects and remains one of the most widely used methods today. This approach follows well-defined stages: definition, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
In this framework, the project’s time and budget are variable, while requirements remain fixed. Because of its linear nature, the method greatly limits going back between phases. It is therefore crucial to clearly define the specifications and the client’s needs from the start. Once the plan is set, the project manager applies each stage strictly, since every task must be completed before the next can begin.
One of the main advantages of this approach is that it reduces risk: if the plan is followed scrupulously, budget and schedule overruns are avoided.
The Waterfall method: the emblematic model
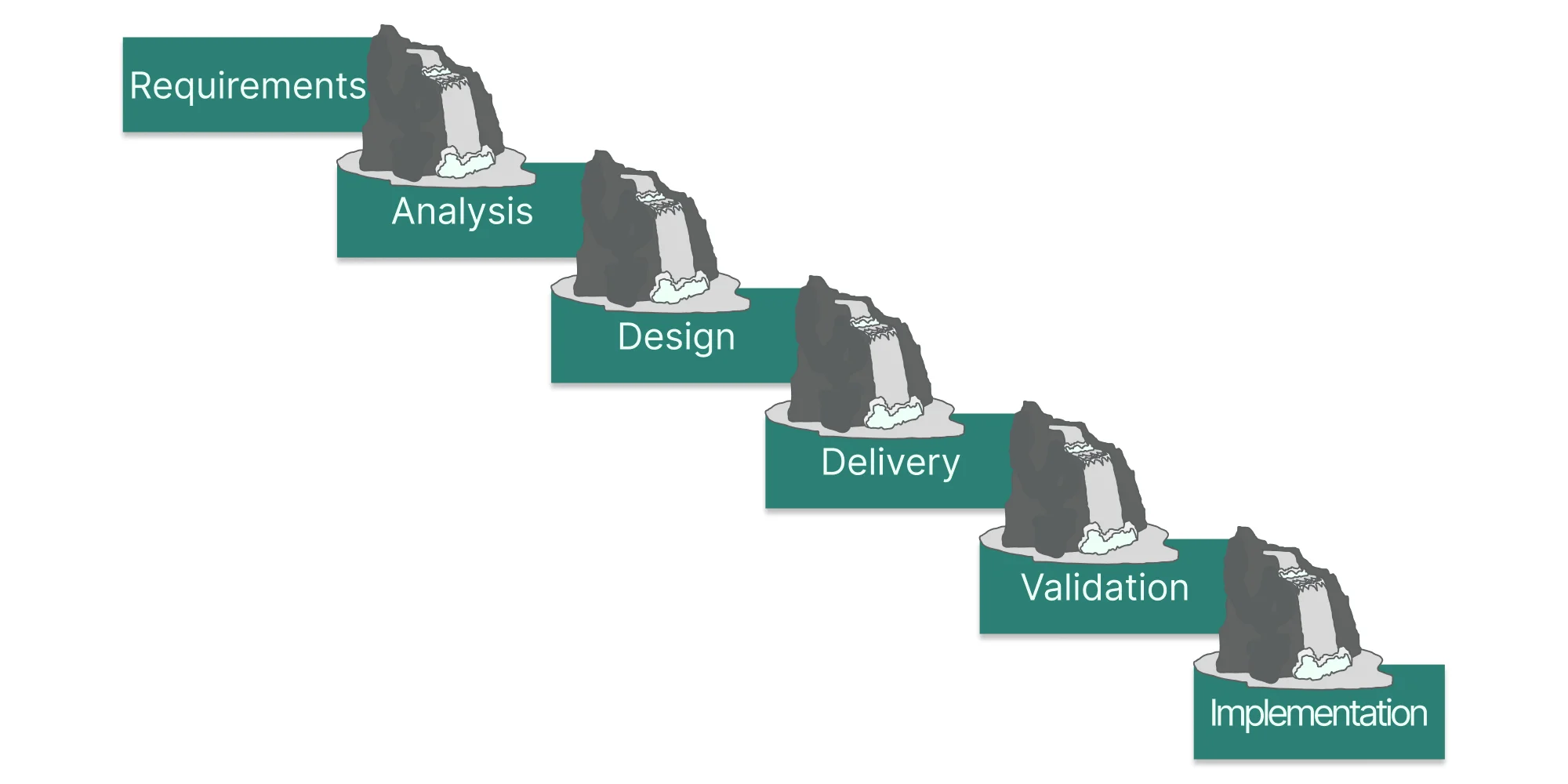
The Waterfall method is the perfect example of this traditional approach. It is a strictly linear method where each phase fully depends on the previous one.
Because it is hard to go back, the method is often seen as rigid—sometimes called the “tunnel effect”.
It is ideal for small projects where the client is certain about the desired final product.
Learn more about the Waterfall method
The V-Model: an improved alternative to Waterfall
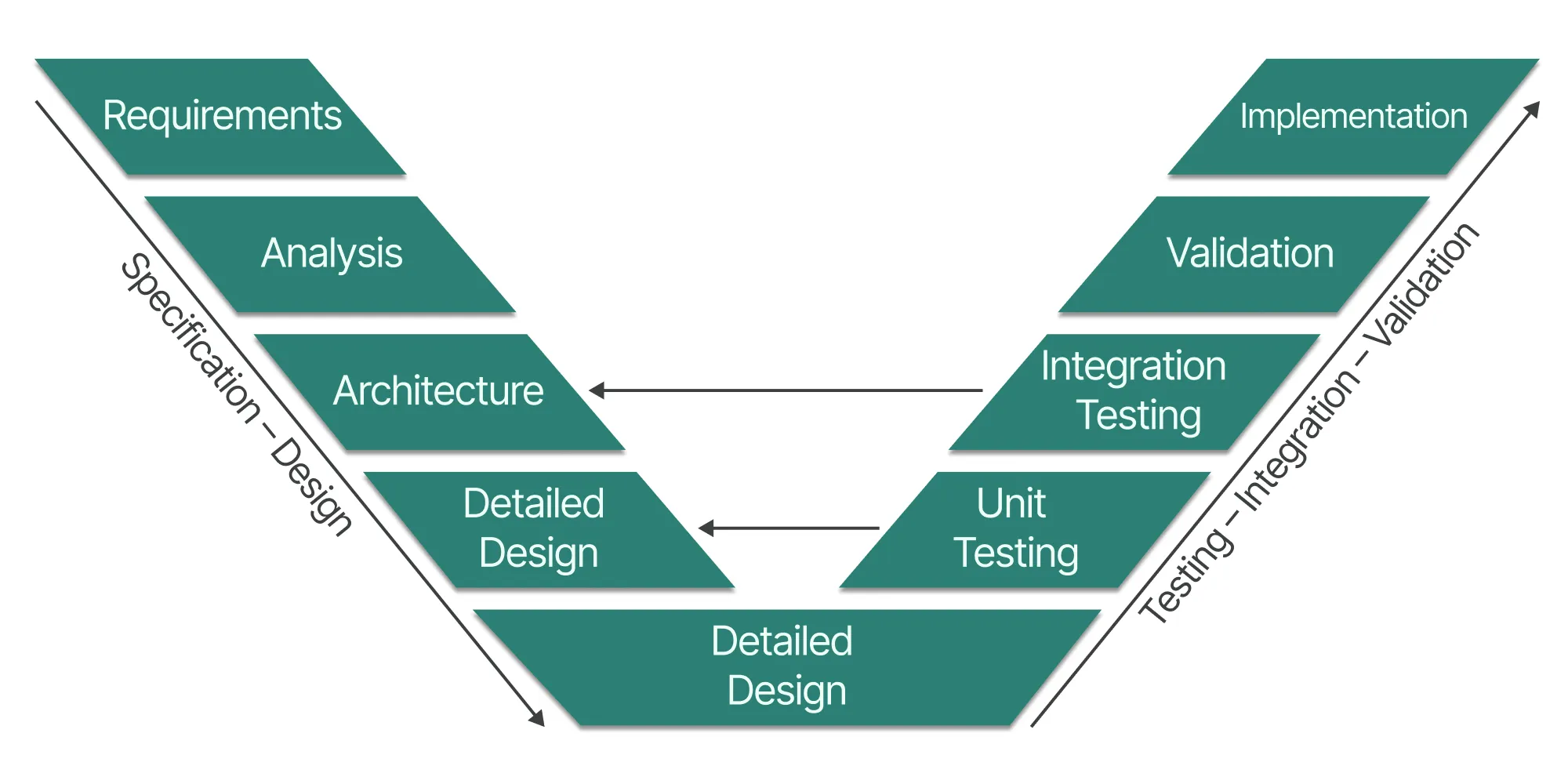
The V-Model evolved from Waterfall to address its main limitations. Unlike Waterfall, this approach allows going back, offering greater flexibility.
The project is no longer treated as a single block delivered all at once, but as a system composed of multiple elements called components. Visually, the method takes the shape of a “V”: the descending phases, similar to Waterfall, are followed by ascending phases to validate the project step by step through various tests involving the client.
The V-Model is particularly suited to projects with substantial budgets and experienced teams where the client has a clear vision, yet gradual adjustments are needed to validate expectations.
This method combines the rigor of linear planning with the flexibility required to deliver a successful project that meets client expectations.
The PRINCE2 method: the reference framework
As projects became more complex and diverse, it became necessary to create a universal, structured method capable of managing any type of project, beyond technical or IT fields.
This led to a methodology first called PROMPT in 1979, renamed PRINCE in 1989, and refined into PRINCE2 in 1996. PRINCE2 (Project IN Controlled Environments) is now a structured project management and certification method focused on three essential pillars: organizing, managing, and controlling projects.
The method was developed by a team of specialists with a review committee of 150 public and private organizations.
PRINCE2 provides a highly operational framework for undertaking project management effectively.
PRINCE2 is particularly suited to complex, structured projects that require a clear methodological framework and optimized risk management. It fits organizations seeking a rigorous, methodical approach.
It blends the rigor of formalized management with the adaptability needed to ensure project success in a controlled environment.
Agile: principles and how it works
For several years now, the “Agile” approach to project management has become a major trend. This method originates from the Agile Manifesto, written in 2001 by 17 software development experts.
Today, Agility is no longer limited to software: it spans many domains and project types. Its success is rooted in four core principles:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
However, these principles don’t mean the secondary elements should be neglected. An Agile project still needs a structured framework to avoid drifting into chaos.
Agile relies on an iterative process, where projects are divided into sprints—short, self-contained work cycles. Each sprint delivers a product increment that is immediately presented to the client. This ongoing involvement enables real-time adjustments based on feedback and results.
Agile thus replaces rigid planning with an adaptive approach: the project evolves gradually, integrating new requirements and user expectations. By planning in short cycles and delivering in small increments, teams can regularly gather customer feedback and feed it into subsequent iterations while controlling cost and risk.
This approach is empirical: decisions are taken based on observation and continuous learning, ensuring better responsiveness and constant alignment with customer needs.
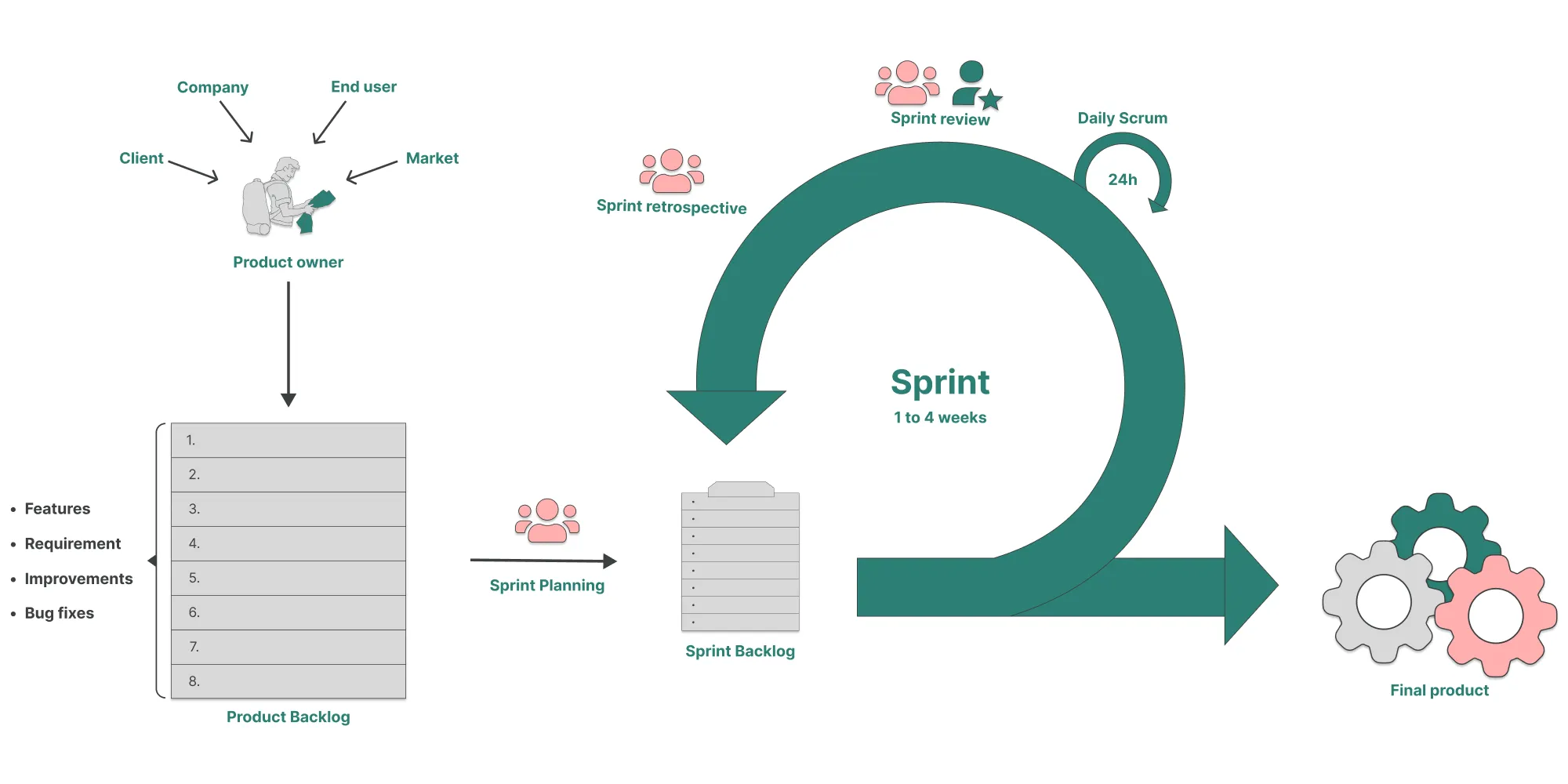
The Scrum method
Scrum is an Agile framework based on collaboration, accountability, and iterative progress. It defines a set of events, artifacts, and roles that work together to help teams structure and manage their work.
Scrum is especially suitable for evolving, complex, and uncertain projects that require strong responsiveness and close collaboration between teams and stakeholders. It excels in environments where needs can change frequently and continuous improvement is essential.
This method combines a structured framework with flexibility to foster adaptability, maximize delivered value, and ensure regular delivery of working features.
Kanban boards: a visual approach to agile management
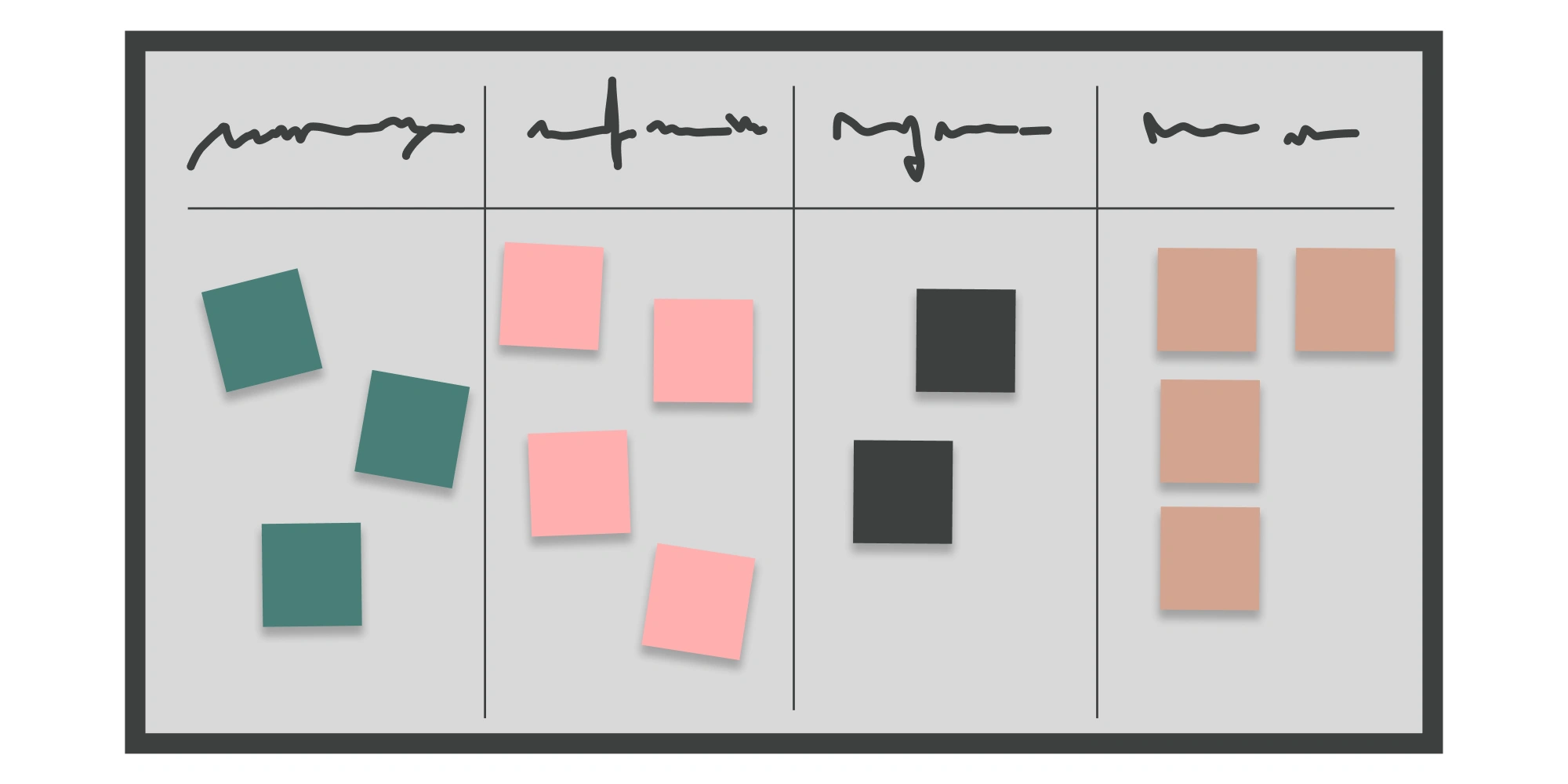
The Kanban method—its name meaning “signboard” in Japanese—is a work-management approach developed in Japanese companies in the 1950s. It relies on a system of cards representing tasks, placed on a board according to their progress. These cards move from one column to another throughout the process, providing a clear visualization of the workflow. Today, Kanban applies across many management domains: from project tasking to inventory, HR, and customer relationship management.
In project management, Kanban lets each team member see at a glance their tasks and the progress of others’ work. It also enables real-time updates of work in progress, ensuring better coordination and communication within the team. It helps spot delays, bottlenecks, and obstacles that might slow down the project.
It is often used alongside other methods when projects are complex with strong interdependencies.
Kanban is ideal for projects needing flexible, visual task management. It suits organizations where transparency, responsiveness, and continuous improvement are priorities, and fits particularly well where tasks can progress independently.
This method combines simplicity with visualization of work in progress to facilitate collaboration and avoid overload.
Learn more about Kanban boards
Lean Management: the art of maximizing value
Inspired by the Japanese production system, Lean Management is an organizational method aimed at eliminating waste that undermines the effectiveness and performance of a team, project, or company. Its goal is to maximize quality while reducing cost, time, and resources. To do so, it relies on integrating the customer into processes to identify what truly creates value, as well as on continuous improvement and optimization of practices and organizational capabilities.
Problem-solving happens directly in the field, involving those closest to the work—best placed to identify waste and propose suitable solutions. This approach requires constant learning across both productive and non-productive activities. More than a method, Lean is a true philosophy that demands shared commitment from teams and leadership, based on common values and close collaboration. Each success becomes a learning opportunity; each problem, a chance to improve. One key challenge is balancing waste reduction with maintaining optimal working conditions.
Lean Management is ideal for projects with limited resources and recurring processes from one project to another, requiring continuous optimization and shorter lead times while ensuring high quality.
It fits organizations where communication between teams and management is fluid, where customers are available to engage in continuous improvement, and where the culture encourages questioning and adaptability in the face of change and challenges.
Lean blends a pragmatic approach with a philosophy of continuous improvement to streamline processes, foster team engagement, and optimize end-to-end workflows.
Learn more about Lean Management
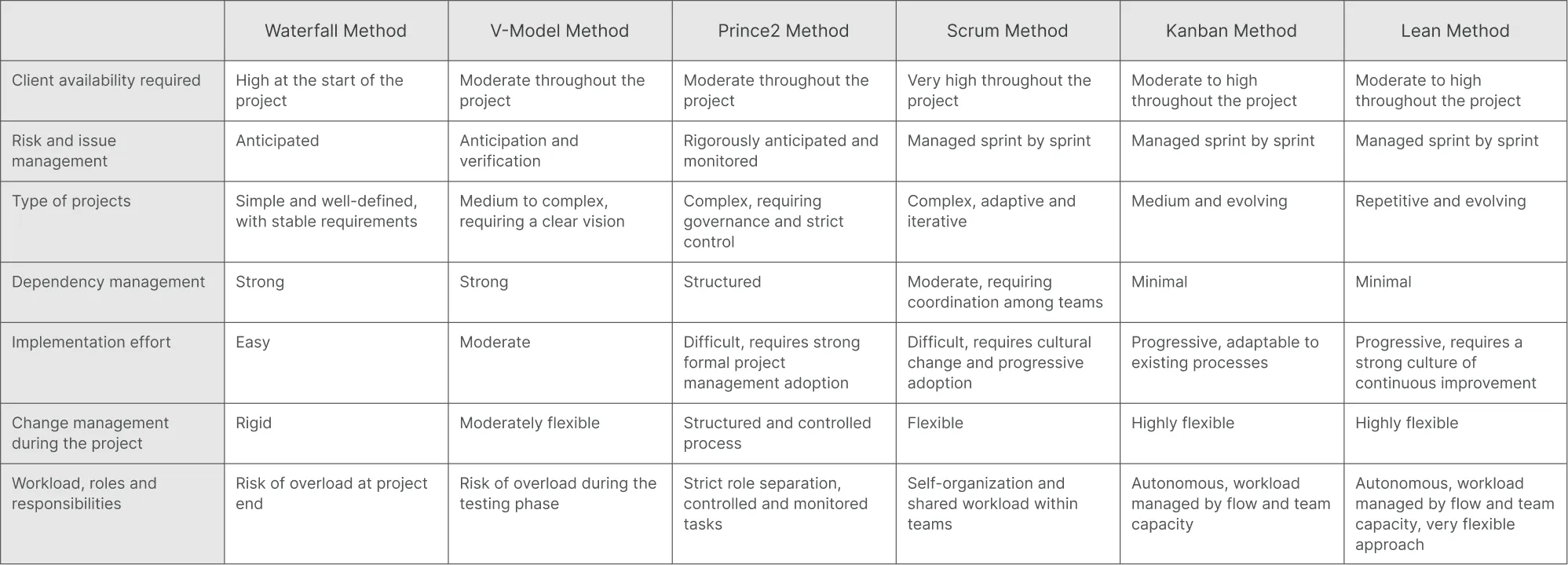
Comparing project management methodologies
Orchesia: a flexible solution to structure and apply your methods
Structure your project effectively
As we’ve seen throughout this article, the fundamentals stay the same regardless of the chosen method: a project must be broken down into objectives, deliverables, and tasks. That work can be done upfront (traditional) or iteratively (Agile/Lean).
With Orchesia, we offer a visual mind-map tool designed to make this project breakdown easier and ensure nothing is missed. This approach helps you structure the project while involving your client in expressing needs.
Understand and optimize your project’s organization
Beyond task decomposition, it’s essential to visualize dependencies between teams, deliverables, and project stages. Workflow mapping plays a key role in success by optimizing activity sequences and avoiding blockers.
Thanks to our dependency-management tool, Orchesia supports this effort by giving you a clear view of interactions between project phases. You can sequence tasks, anticipate risks, and adjust priorities based on constraints and available resources.
Facilitate communication and collaboration
One of the main challenges in project management, regardless of method, is ensuring smooth communication among all stakeholders: clients, vendors, internal teams, and partners.
With Orchesia, organizing and sequencing tasks leads to dynamic tracking views tailored to each user’s needs:
- To-Do / Backlog view to see all tasks to be completed
- Gantt view to plan and monitor project evolution over time
- Kanban view for visual, flow-based work management
Each task is collaborative, editable in real time, and centralizes documents, comments, and updates. No more juggling tools: everything essential is in one place, ensuring perfect alignment across teams.
Track and steer in real time
Whatever framework you adopt, measuring performance and verifying that delivered work creates value—while meeting deadlines and budgets—is critical.
With Orchesia, you have a personalized dashboard to track your project KPIs in real time. Through an intuitive interface, you can:
- Track KPIs using custom fields and tailored visualizations
- Compare data over time to identify trends and variances
- Analyze workflows to find bottlenecks and reprioritize.
This 360° view allows you to lead teams effectively, anticipate risks, and make informed decisions.
A solution that fits every methodology
Whether you use a traditional approach (Waterfall, V-Model, PRINCE2) or a more agile one (Scrum, Kanban, Lean), Orchesia helps you structure, plan, and steer your projects with rigor and efficiency.
Ultimately, whatever methodology you adopt, Orchesia provides a solid yet flexible framework tailored to your organization’s needs. By making collaboration, planning, and performance tracking easier, our software helps transform your project management.
Try our project management software Orchesia free for two weeks, no commitment!